A furnace that refuses to start can turn a cold day into a stressful situation in a hurry. When heat does not arrive after adjusting the thermostat, many homeowners immediately worry about major repairs. In reality, several common issues can prevent a furnace from igniting, and some are simple to identify before calling for emergency service.
Understanding how gas, combustion, airflow, and safety components work together can help you recognize what may be happening. If your furnace is not igniting, the steps below can help you narrow down the cause while keeping safety as the top priority.
Start With Safety Before Troubleshooting
Any issue involving a gas furnace deserves caution. Combustion systems rely on controlled flame, proper ventilation, and sealed connections to operate safely.
If you smell gas, hear hissing near a pipe, or suspect a leak, stop immediately and contact a professional. Carbon monoxide risks increase when a furnace is not lighting correctly, especially if the flue or chimney is blocked. Carbon exposure can affect indoor air quality and health long before visible symptoms appear.
Check the Thermostat and Power Supply
Before assuming the furnace itself has failed, confirm that it is receiving the signal to start.
Thermostat Settings Matter
Set the thermostat to heat and raise the temperature several degrees above the current room reading. A smart thermostat can lose connection or experience software issues that interrupt communication with the heating system. Low battery voltage or wiring problems can also prevent the ignition system from activating.
If your furnace is not igniting but the thermostat display looks normal, switch it off and back on to reset the signal. This simple step often resolves communication issues.
Confirm the Furnace Has Power
Check the furnace switch, circuit breaker, and any nearby shutoff points. A tripped breaker or switched-off unit can mimic more serious problems. This step is especially important in utility rooms, attics, or basements where switches are easily bumped.
Inspect the Airflow and Air Filter
Restricted airflow can prevent a safe ignition. Furnaces are designed to stop the flame if the airflow is inadequate. A clogged air filter is a frequent culprit when your furnace won’t ignite. Reduced airflow causes heat buildup, triggering safety sensors that shut down the system. Replace the air filter if it appears dirty or overdue for maintenance.
You should also check that vents and ducts are not blocked by furniture or debris. Poor airflow affects temperature balance and places extra strain on the heating system.
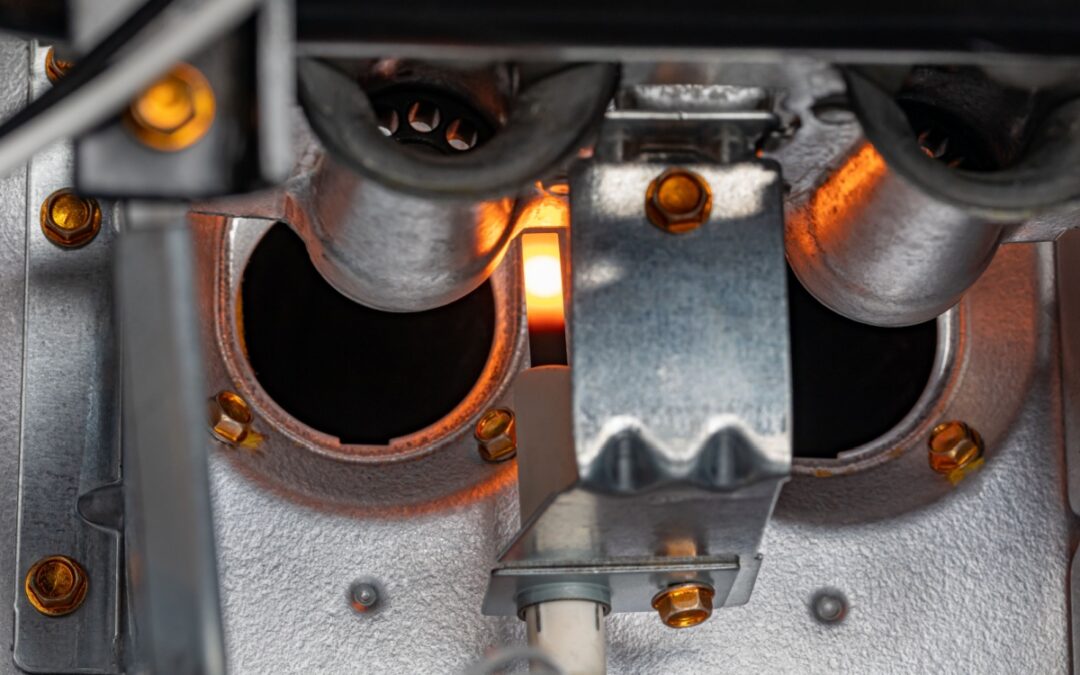
Pilot Light and Ignition System Issues
Older furnaces rely on a pilot light, while newer models use electronic ignition systems. Both can fail for different reasons.
Pilot Light Problems
If the pilot light is out, the furnace will not light. Drafts, dust buildup, or a failing thermocouple can cause the flame to go out. A thermocouple senses heat from the pilot light and signals the gas valve to open. If it fails, gas flow stops as a safety measure.
Electronic Ignition Failures
In modern systems, a faulty igniter can cause issues with the furnace’s regular operations. Cracks, wear, or electrical faults can prevent the igniter from heating enough to start combustion.
Gas Supply and Valve Concerns
A furnace requires steady access to natural gas to ignite. Any interruption along the supply path can stop the process.
Check that the gas valve near the furnace is open. If other gas appliances, such as a stove or fireplace, are not working, the issue may extend beyond the furnace. This can point to a broader supply problem or meter issue.
If you suspect your furnace is not igniting due to supply issues, contact a professional right away. Attempting to adjust valves or pipes without training can be dangerous.
Sensors and Safety Switches Can Stop Ignition
Modern furnaces rely on sensors to verify safe operation before allowing a flame to continue. A dirty flame sensor may fail to detect combustion, causing the furnace to shut down seconds after ignition. This often leads to reports that the furnace won’t light or ignite, even though the unit tries to start.
Ventilation and Exhaust Problems
Combustion produces exhaust gases that must be safely vented from the home. Blocked ventilation can stop ignition entirely.
Check for visible obstructions around the flue or chimney, especially after storms or heavy debris buildup. Ice, nests, or collapsed duct sections can interfere with exhaust flow. Poor ventilation can lead to carbon buildup, which the system detects and reacts to by shutting down.
When to Call for Professional Help
If your furnace won’t ignite after basic troubleshooting, professional service becomes necessary. Repeated ignition attempts, clicking sounds without flame, or complete silence from the unit all signal the need for expert attention.
Ignoring these signs can escalate minor problems into larger furnace repairs. A trained technician can test the ignition system, inspect the pump, check pressure levels, and confirm safe combustion operation.
Schedule Service With Efficient Air Heating and Cooling
If your furnace is not igniting, Efficient Air Heating and Cooling is ready to help. Our technicians handle all furnace issues, including sensor failures, airflow problems, and ignition system repairs with care and accuracy.
Do not let a heating problem compromise comfort or safety. Contact Efficient Air Heating and Cooling today to schedule service and restore reliable heat to your home.

Recent Comments